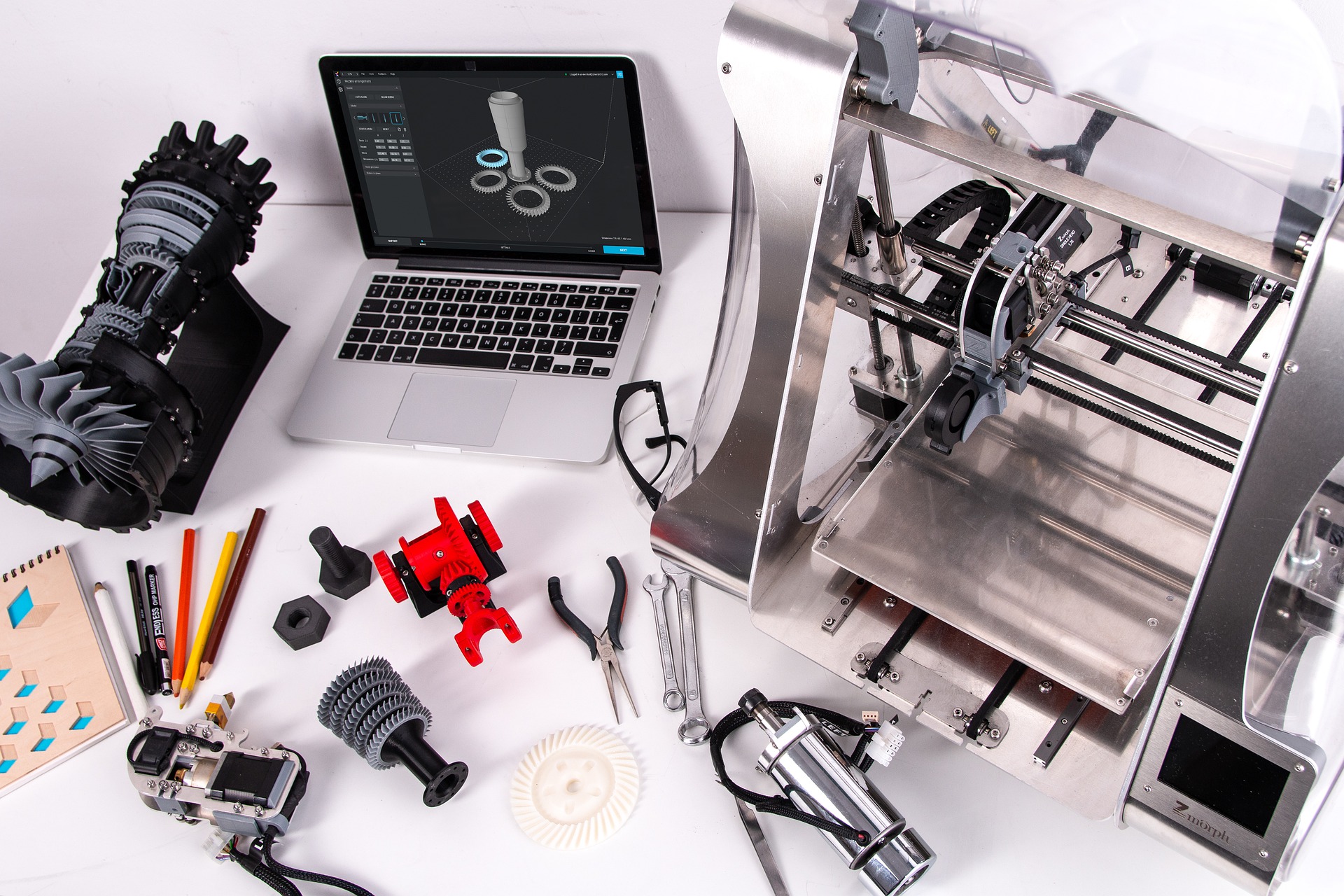
3D-printable, 4D-applicable electroactive structures from Diamond-Reinforced polylactide Composites
4D-DRC
3D-printable, 4D-applicable electroactive structures from Diamond-Reinforced polylactide Composites
The project focuses on the development of 3D printing technology with the use of polylactide reinforced with conductive nanodiamonds, enabling the development of an electrode material for electroanalytical purposes and 4D smart materials with characteristics modifiable by environmental factors. The second goal of the project is the construction of free-standing sensory systems (microelectrode arrays and flow-injection cells) and actuators. Micromechanical and rheological interactions of composites will be studied, the mechanisms of charge transfer in the volume of the material and on its surface. The main goal of the work concerns the determination and design of the stability of nanomechanical and electrochemical parameters of the composite, in terms of its use in accordance with the concept of intelligent 4D materials, including microelectrode matrix systems and flow sensors. The project was financed by the National Science Centre in SONATA BIS call (2020/38/E/ST8/00409).
Members

Miss Agata Smułka
PhD student - scholarPh.D. Student at Faculty of Chemistry, UG, experienced in spectroscopy analysis and electrode functionalization for analytical purposes. Within the project responsible for the electrochemical characterization of new composite materials.

Miss Kornelia Kozłowska
M.Sc. student - scholarM.Sc. student at Faculty of Chemistry, UG, experienced in electroanalysis of organic compounds. Within the project responsible for the electrochemical characterization of new composite materials.
News
Resources

Robert Bogdanowicz, Jacek Ryl
Current Opinion in Electrochemistry
Structural and electrochemical heterogeneities of boron-doped diamond surfaces
In this mini-review, we discuss the recent findings on different types of electric and structural heterogeneities of boron-doped diamond and its derivatives. The effects of grain size, different crystal facets, boron concentration or sp2/sp3-carbon share are crucial to understanding BDD's electrochemical characteristics.

Adrian Koterwa, Iwona Kaczmarzyk, Szymon Mania, Mateusz Cieslik, Robert Tylingo, Tadeusz Ossowski, Robert Bogdanowicz, Pawel Niedzialkowski, Jacek Ryl
Applied Surface Science
The role of electrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis treatment in the enhancement of the electrochemical properties of 3D-printed carbon black/poly(lactic acid) structures
In this work, we have presented and compared various strategies of CB-PLA electrodes activation, including the hydrolysis and electrolysis in acidic and alkaline media as well as enzymatic activation by proteinase K. We have also presented and discussed the synergistic enzyme and electrolysis interaction, leading to surface activation by electropolymerization. Importantly, we have confirmed the most efficient electrolysis conditions for successful electrode activation.

Jacek Ryl, Pawel Niedzialkowski, Robert Bogdanowicz
International Workshop on Functional Nanostructured Materials - "FuNaM-3"
Boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes as electrochemical sensors
The presentation describes some of the challenges concerning the utilization of BDD electrodes for electroanalysis as well as the successful BDD-based sensor implementations by our groups.

Maciej J. Głowacki, Mateusz Cieślik, Mirosław Sawczak, Adrian Koterwa, Iwona Kaczmarzyk, Rafał Jendrzejewski, Łukasz Szynkiewicz, Tadeusz Ossowski, Robert Bogdanowicz, Paweł Niedziałkowski, Jacek Ryl
Applied Surface Science
Helium-assisted, solvent-free electro-activation of 3D printed conductive carbon-polylactide electrodes by pulsed laser ablation
In this article we present a world-first approach to C-PLA 3D-printed electrodes activation by pulsed laser ablation, increasing their electrochemical activity. We have optimized the ablation parameters and found the highest electroanalytical performance to be found if ablation is carried out in He atmosphere. The caffeine detection with CV and DPV was done as the proof of concept for our procedure.